

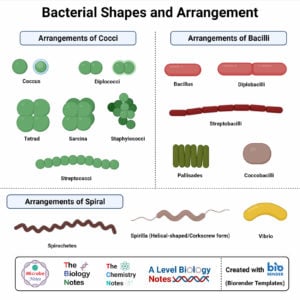
(credit “Coccus”: modification of work by Janice Haney Carr, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention credit “Coccobacillus”: modification of work by Janice Carr, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention credit “Spirochete”: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) Note how coccobacillus is a combination of spherical (coccus) and rod-shaped (bacillus). See Table 1.1 for units of length used in microbiology.įigure 1.13 Common bacterial shapes. Bacterial cells are typically about 1 µm, and viruses can be 10 times smaller than bacteria ( Figure 1.12). For some perspective, consider that a typical animal cell measures roughly 10 µm across but is still microscopic. An object must measure about 100 micrometers (µm) to be visible without a microscope, but most microorganisms are many times smaller than that. However, there are some unicellular microbes that are visible to the naked eye, and some multicellular organisms that are microscopic. Most microbes are unicellular and small enough that they require artificial magnification to be seen. Provide an overview of the field of microbiology.Describe the similarities and differences between archaea and bacteria.
Give examples of different types of cellular and viral microorganisms and infectious agents.List the various types of microorganisms and describe their defining characteristics.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
